📝 Note (Updated 2025)
This guide uses Tyk v5.6.1 and Elasticsearch 7.17.26 from March 2024. Check Tyk’s documentation for the latest versions and features. The architecture and setup approach remain valid.
1. Introduction
Tyk is an API gateway solution, and its open-source version is powerful with many features. Compared to other alternatives, it allows you to set up and manage APIs for free using the API gateway.
- Setting up tyk gateway
- Setting up tyk pump
- Setting up elasticsearch and kibana
We’ll proceed with everything using docker compose.
2. Configuration
We’ll create it with docker compose, and the following components are needed:
redis:latest
tykio/tyk-gateway:v5.6.1
tykio/tyk-pump-docker-pub:v1.11.1
elasticsearch:7.17.26
docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.26Let’s create a docker compose file containing all of these, and prepare the necessary configurations separately.
1. redis
fill compose.yaml file with the following:
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
network_mode: host
environment:
- REDIS_PASSWORD=${REDIS_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- ./mnt:/bitnami/redis/data
restart: alwaysWe set the redis password in the .env file for added security, and you need to know the password to access it.
2. tyk gateway
services:
tyk-gateway:
image: tykio/tyk-gateway:v5.6.1
network_mode: host
environment:
- TYK_GW_SECRET=${TYK_GW_SECRET}
- TYK_GW_ENABLEHASHEDKEYSLISTING=true
- TYK_DB_REDISPASSWORD=${REDIS_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- ./config/tyk.standalone.conf:/opt/tyk-gateway/tyk.conf
- ./config/apps:/opt/tyk-gateway/apps
- ./config/policies:/opt/tyk-gateway/policiesBesides this file, three more files are needed.
tyk.conf
This is the configuration file needed for tyk’s overall operation.
{
"log_level": "info",
"listen_port": 8080,
"secret": "352d20ee67be67f6340b4c0605b044b7",
"template_path": "/opt/tyk-gateway/templates",
"tyk_js_path": "/opt/tyk-gateway/js/tyk.js",
"middleware_path": "/opt/tyk-gateway/middleware",
"use_db_app_configs": false,
"app_path": "/opt/tyk-gateway/apps/",
"storage": {
"type": "redis",
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 6379,
"username": "",
"database": 10,
"optimisation_max_idle": 2000,
"optimisation_max_active": 4000
},
"enable_analytics": true,
"analytics_config": {
"enable_detailed_recording": true,
"type": "",
"ignored_ips": []
},
"health_check": {
"enable_health_checks": false,
"health_check_value_timeouts": 60
},
"enable_non_transactional_rate_limiter": true,
"enable_sentinel_rate_limiter": false,
"enable_redis_rolling_limiter": false,
"allow_master_keys": false,
"policies": {
"policy_source": "file",
"policy_path": "/opt/tyk-gateway/policies"
},
"hash_keys": false,
"close_connections": false,
"http_server_options": {
"enable_websockets": true
},
"allow_insecure_configs": true,
"coprocess_options": {
"enable_coprocess": true,
"coprocess_grpc_server": ""
},
"enable_bundle_downloader": true,
"bundle_base_url": "",
"global_session_lifetime": 100,
"force_global_session_lifetime": false,
"max_idle_connections_per_host": 500,
"enable_jsvm": true
}policies.json
{
"my-policy": {
"active": true,
"name": "my-policy",
"rate": 1000,
"per": 1,
"quota_max": 10000,
"quota_renewal_rate": 3600,
"access_rights": {
"api-version": {
"api_name": "api-version",
"api_id": "api-version",
"versions": [
"Default"
],
"allowed_urls": [],
"limit": null,
"allowance_scope": ""
}
},
"tags": [
"Startup Users"
]
}
}apps
Place the necessary API configurations in the apps directory
{
"name": "my-api-version",
"api_id": "my-api-version",
"org_id": "onec",
"definition": {
"location": "header",
"key": "version"
},
"auth": {
"auth_header_name": "my-api-token"
},
"version_data": {
"not_versioned": true,
"versions": {
"Default": {
"name": "Default"
}
}
},
"proxy": {
"listen_path": "/version",
"target_url": "https://myapp/version/",
"strip_listen_path": true
}
}3. Managing API Keys
API keys are registered with the tyk gateway api, and the keys are stored. Here you can configure things like Rate Limiting. The payload to use for the Gateway API is as follows:
{
"allowance": 1000,
"rate": 500,
"per": 1,
"expires": -1,
"quota_max": -1,
"quota_renews": 1449051461,
"quota_remaining": -1,
"quota_renewal_rate": 60,
"org_id": "onec",
"access_rights": {
"my-api-version": {
"api_name": "api-version",
"api_id": "api-version",
"versions": [
"Default"
],
"allowed_urls": [],
"limit": null,
"allowance_scope": ""
}
}
}
}
3. tyk pump
To analyze APIs and charge users, we need to know which APIs are being called. The pump’s role is to transfer the contents to another service when someone makes an API call.
compose.yaml
tyk-pump:
image: tykio/tyk-pump-docker-pub:v1.11.1
network_mode: host
environment:
- TYK_PMP_LOGLEVEL=info
- TYK_DB_REDISPASSWORD=${REDIS_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- ./config/pump.conf:/opt/tyk-pump/pump.conf
- ./mnt:/mnt
user: 1000:1000
The pump’s operation can be configured in the pump.conf file, and in this example, it’s configured to send results to elasticsearch.
pump.conf
{
"analytics_storage_type": "redis",
"analytics_storage_config": {
"type": "redis",
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 6379,
"hosts": null,
"username": "",
"database": 10,
"optimisation_max_idle": 100,
"optimisation_max_active": 100,
"enable_cluster": false
},
"purge_delay": 2,
"pumps": {
"elasticsearch": {
"type": "elasticsearch",
"meta": {
"index_name": "tyk_analytics",
"elasticsearch_url": "http://elasticsearch:9200",
"enable_sniffing": false,
"document_type": "tyk_analytics",
"rolling_index": false,
"extended_stats": true,
"decode_base64": true,
"version": "7",
"bulk_config": {
"workers": 2,
"flush_interval": 60
}
}
}
},
"dont_purge_uptime_data": true
}
4. Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch receives data from the pump and processes it for easy searching.
compose.yaml
services:
elasticsearch:
image: elasticsearch:7.17.26
network_mode: host
environment:
- discovery.type=single-node
- xpack.security.enabled=false
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
volumes:
- ./mnt:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
Instead of separate configuration, we set a few things through environment variables.
4. Kibana
Kibana is used to transform the data received from elasticsearch into a visually appealing format.
compose
services:
kibana:
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.26
network_mode: host
environment:
- ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://127.0.0.1:9200
- ELASTICSEARCH_URL=http://127.0.0.1:9200
# - KIBANA_PASSWORD=${KIBANA_PASSWORD}
- SERVERNAME=kibana
- SERVER_PUBLICBASEURL=https://kibana.mycompany.com
volumes:
- ./config/kibana.yaml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.ymlkibana.yaml
server.port: 5601If everything works well, you can see the following screen in kibana.
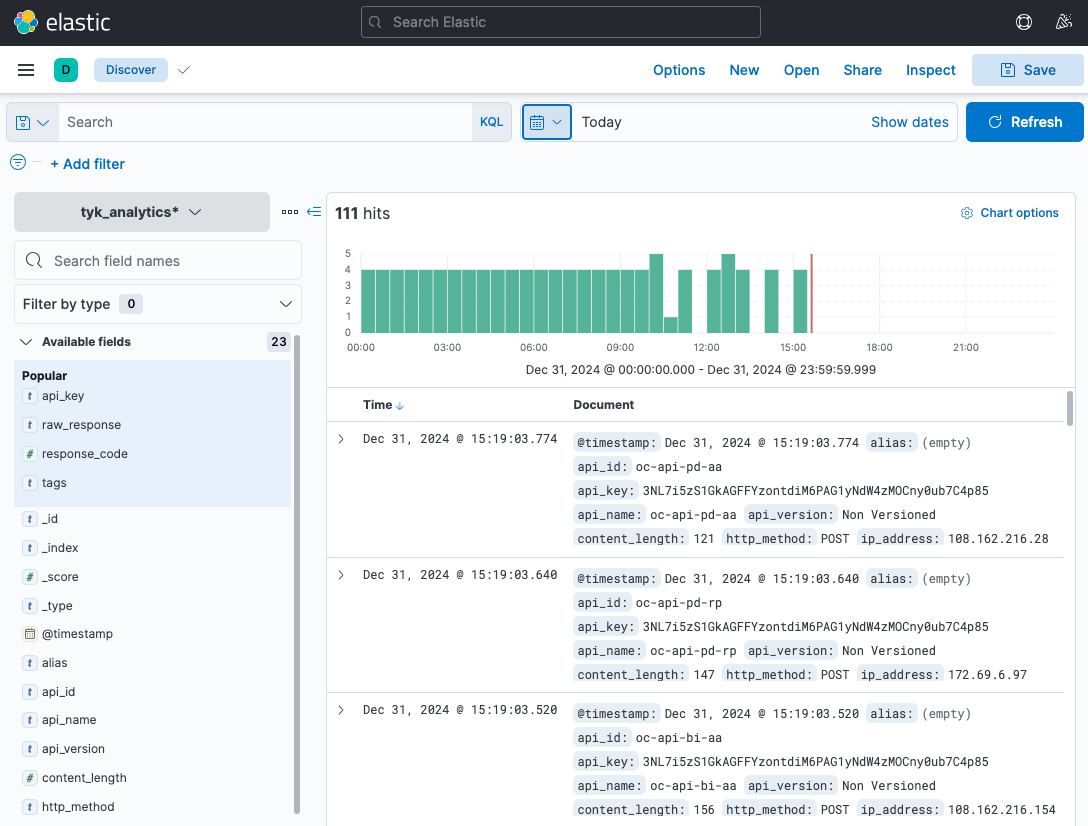
3. Conclusion
We set up a free and simple tyk gateway using docker compose, and checked the API usage results through kibana via pump.

